Information Technology (IT)
This is how the “Shell Shock” bug imperils the whole internet
It’s a hacker’s wet dream: a software bug discovered in the practically ubiquitous computer program known as “Bash” makes hundreds of millions of computers susceptible to hijacking. The impact of this bug is likely to be higher than that of the Heartbleed bug, which was exposed in April. The National Vulnerability Database, a US government system which tracks information security flaws, gave the bug the maximum score for “Impact” and “Exploitability,” and rated it as simple to exploit.
The bug, which has been labeled “Shell Shock” by security experts, affects computers running Unix-based operating systems like Mac OS X and Linux. That means most of the internet: according to a September survey conducted by Netcraft, a British internet services company, just 13% of the busiest one million websites use Microsoft web servers. Almost everyone else likely serves their website via a Unix operating system that probably uses Bash.
Microsoft’s Bing Predicts correctly forecasted the Scottish Independence Referendum vote
Bing Predicts was beta tested in the UK for this referendum. The prediction engine uses machine-learning models to analyse and detect patterns from a range of big data sources such as the web and social activity in order to make accurate predictions about the outcome of events.
Bing got the yes/no vote right, but missed the size of the vote to stay united with England, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
Is the profession of science broken (a possible cause of the great stagnation)? Fascinating discussion which mirrors many friends’ comments that too much time is taken up applying for and administering grants, and not enough time is left for the actual research, for unconventional ideas.
What has changed is the bureaucratic culture. The increasing interpenetration of government, university, and private firms has led everyone to adopt the language, sensibilities, and organizational forms that originated in the corporate world. Although this might have helped in creating marketable products, since that is what corporate bureaucracies are designed to do, in terms of fostering original research, the results have been catastrophic.
Climate
Climate Science Is Not Settled The Wall Street Journal piece by a former Obama adviser and BP scientist inflamed the commentariat, after publication September 16, on the eve of the big climate talks and march in New York City. See On eve of climate march, Wall Street Journal publishes call to wait and do nothing for a critical perspective.
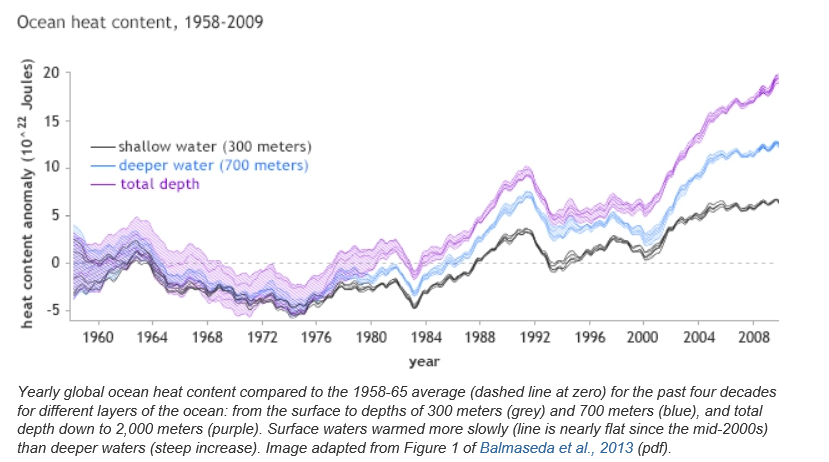
This chart, from NOAA, is one key – showing the divergence in heat stored in various layers of the oceans –
Nicholas Stern: The state of the climate — and what we might do about it TED talk.
Ebola
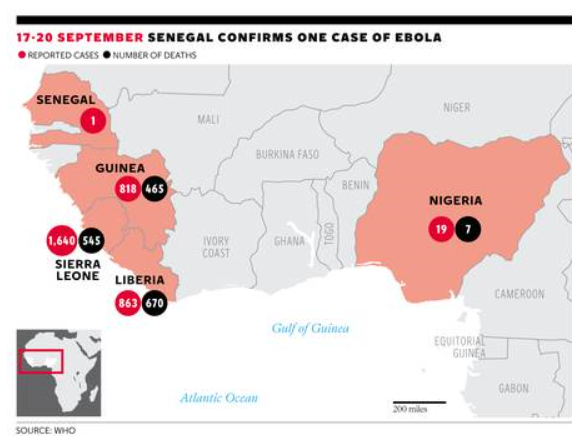
The public response to the Ebola epidemic is ramping up, but the situation is still dire and total cases and deaths are still increasing exponentially.
Ebola outbreak: Death toll passes 3,000 as WHO warns numbers are ‘vastly underestimated’
“The Ebola epidemic ravaging parts of West Africa is the most severe acute public health emergency seen in modern times.Never before in recorded history has a biosafety level four pathogen infected so many people so quickly, over such a broad geographical area, for so long.”
Global Economy
What Does a ‘Good’ Chinese Adjustment Look Like? Michael Pettis argues that what some see as a “soft landing” is in fact a preparation for later financial collapse. Instead, based on an intricate argument regarding interest rates and the nominal GDP growth rates in China, he proposes a reduction in Chinese GDP growth going forward through control of credit – in order to rebalance the Chinese consumer economy. Pettis is to my way of thinking always relevant, and often brilliant in the way he makes his analysis.
What Went Wrong? Russia Sanctions, EU, and the Way Out
Washington, Brussels and Moscow are in a vicious circle, which would spare none of them and which has potential to undermine global recovery.
Venture Capital